Conditionals: Definition, Structure & Examples
(5/5, 72 votes)
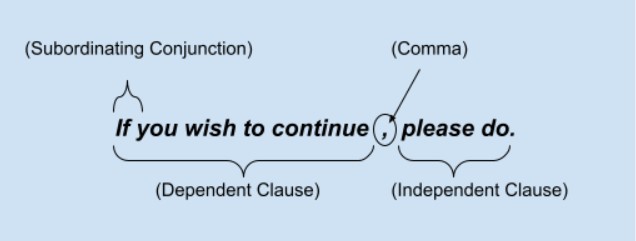
Normally conditional sentences are called conditionals. These sentences usually contain the conjunction IF. Sometimes they are called 'if clauses'.
Types of Conditionals
There are mainly two types of conditionals:
The real conditionals
The real conditionals express factual or habitual conditions which have the possibility to occur in the future or generally occur in the present.
Example:
- I’ll go if you give me the ball.
- If I feel better, I’ll certainly play.
- If you do well in the exams, I’ll buy you a gift.
Structures of the Real Conditionals:
| For Future Conditions |
| If + subject + simple present tense + subject + will/can/may/must + verb in base form. . . Subject + will/can/may/must + verb in base form. . . + if + subject + simple present tense |
Example:
|
| For Habitual Conditions |
| If + subject + simple present tense + subject + simple present tense. . . Subject + simple present tense + if + subject + simple present tense. . |
Example:
|
| For Commands |
| If + subject + simple present tense + command form (simple present) . . . . . Command form (simple present). . . . . + if + subject + simple present tense. |
Example:
|
The unreal conditionals
The unreal conditionals express hypothetical conditions which have no possibility to occur in the past, present or future but describe what could/might have occurred supposedly.
Example:
- If I were rich, I would travel my whole life.
- If I had a car, I could go anywhere.
- If we had not missed the train, we would have reached the city.
Structures of Unreal Conditionals:
| For Present/Future Conditions |
| If + subject + simple past tense + subject + would/could/might + verb in base form. . . subject + would/could/might + verb in base form + if + subject + simple past tense |
Example:
|
| For Past Conditions |
| If + subject + past perfect tense + subject + would/could/might + have+ verb in past particple form Subject + would/could/might + have + verb in past participle form + if + subject + simple past tense |
Example:
|
Note: There is another structure of unreal conditional which does not use the conjunction if. Had replaces if and creates a conditional sentence.
| Had + subject + verb in past participle + subject + would/could/might + have + verb in past particple |
Example:
|
Published By LearnGrammar.Net
Grammar
Read More
- How to Use "Therefore" in Sentences Avoiding Common Mistakes
- How to Use "Whereas" with Examples and Avoid Common Mistakes
- When and How to Use "Thus" Correctly Without Common Mistakes
- How to Use "On the Contrary" Properly with Meaning and Examples
- When and How to Use "Either/Or" with Examples and Common Mistakes to Avoid
- How to Use "On the Other Hand" Effectively without Mistakes
- How to Use "Respectively" with Example and Common Errors to Avoid
- How and When to Use "Moreover" Without Mistakes
- How to Use "Likewise" in Sentences Based on Context & When not to Use
- When & How to Use "Although" in Sentences to Avoid Mistake