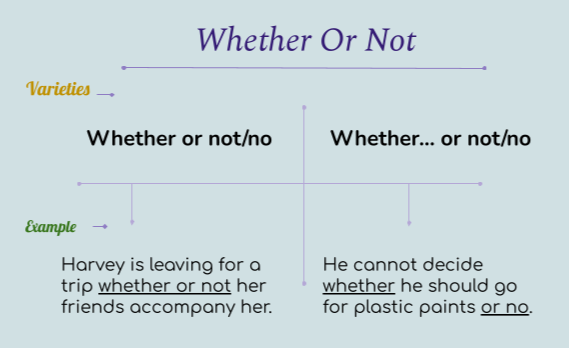
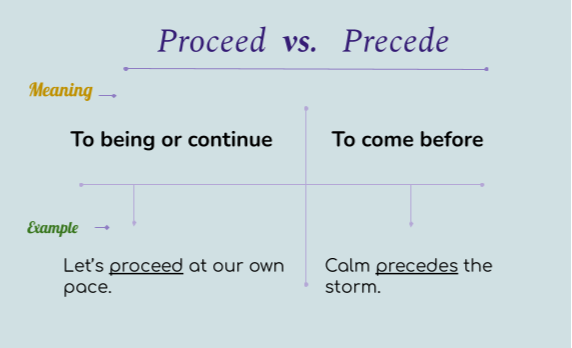
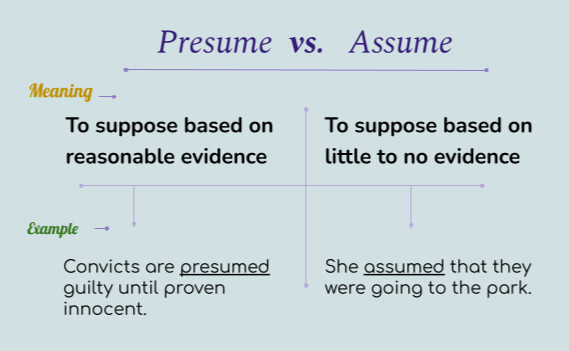
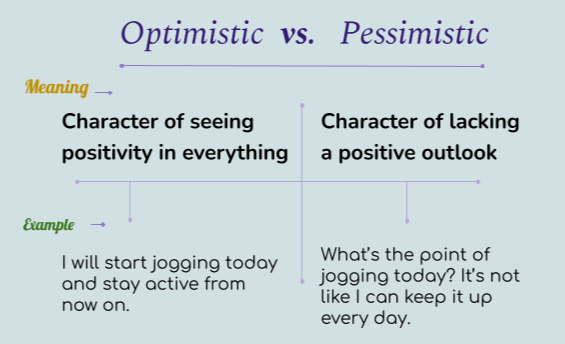
Subjective vs. Objective - Know the Difference

English learners often confuse the difference between Subjective and Objective matters and find it hard to remember what sets them apart. Subjective is the flawed characteristic of opinions that makes them biased and objective is the characteristic of the statement that establishes them as factual truths.
Subjective
Something is labeled subjective when it depends heavily on the feelings, emotions and perspectives of an individual. Subjective remarks are often biased, prejudiced and partial in nature.
Exp. #1 - What you said is merely subjective.
When a statement is subjective, it has room to change or evolve with time and experience. Labeling something as subjective is a constructive way to argue with someone’s opinion.
Exp. #2 - Subjective views vary from person to person.
People’s opinions, views and statements can differ on most occasions and these depended on numerous factors.
Objective
- It is an Adjective and when something is objective, it does not depend on the feelings, emotions and perspectives of anybody. That makes these unbiased, factual and logical.
Exp. #1 - Historians always vow to be objective but it is hardly possible.
Humans are inherently biased and entitled to their own opinions as their outlook on things gets influenced by all the things around them. Historians are often blamed for biased explanations of historical events but since they have a huge responsibility of keeping records of these, they vow to be giving information solely based on facts and that would be objective.
Exp. #2 - Keeping an objective mindset is necessary for societal harmony.
Subjective statements are often the root cause of arguments and disagreements. So, objective remarks that are based on facts are great for peace among fellow humans.
- Objective is a Noun and it means the goal or purpose that is to be achieved.
Exp. #1 - The prime objective of the journey is to get a taste of the new weather.
A traveler willing to explore new weather travels to new places with the goal of experiencing the new types of weather. The goal is their objective.
Exp. #2 - My objective was to just see them one last time before I leave.
One last goodbye can be your aim when it comes to going to meet someone before you leave for a long time. That is an objective too.
Practical Example
Watching the TV series Game of Thrones, James said, “I don’t like it.” He is entailed to have an opinion and allowed to express his likes and dislikes and that is the nature of subjective remarks.
When a professional TV series critic, Mary reviews it and does not like it, she says, “The explicit showcasing of gore and violence aids to the evil and violent desires of the spectators.” Being a psychological analysis based on years of research, Mary’s statement is objective in nature.
Difference between Subjective and Objective
Subjective and Objective are polar opposite terms. Subjective matters have the license to be flawed and narrow in general whereas objective ones lack that liberty. Objective opinions are based on facts and logic and cannot be canceled for being biased or factually inaccurate.
|
Factors |
Subjective |
Objective |
|
Meaning |
Depending on personal opinions and emotions |
Not depending on personal opinions and emotions |
|
Adjective |
Adjective |
|
|
Major Characteristic |
Biased |
Fact |
|
In Sentence |
I don’t like gore and violence. |
Gore and violence in games and movies are not good for the psychological well-being of the spectators. |
Grammar
Read More
- How to Use "Therefore" in Sentences Avoiding Common Mistakes
- How to Use "Whereas" with Examples and Avoid Common Mistakes
- When and How to Use "Thus" Correctly Without Common Mistakes
- How to Use "On the Contrary" Properly with Meaning and Examples
- When and How to Use "Either/Or" with Examples and Common Mistakes to Avoid
- How to Use "On the Other Hand" Effectively without Mistakes
- How to Use "Respectively" with Example and Common Errors to Avoid
- How and When to Use "Moreover" Without Mistakes
- How to Use "Likewise" in Sentences Based on Context & When not to Use
- When & How to Use "Although" in Sentences to Avoid Mistake