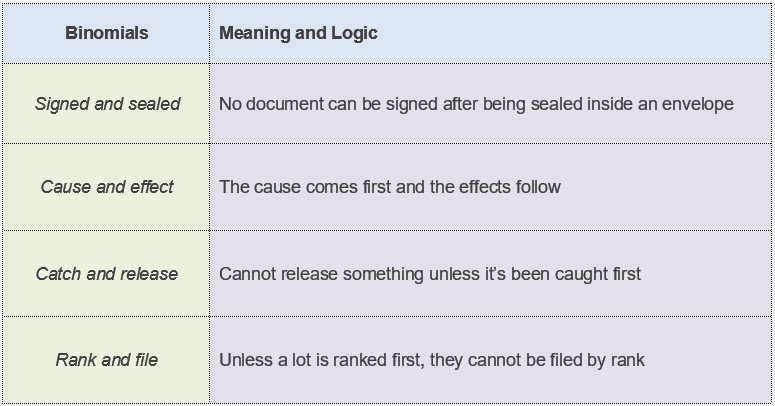
Punctuation: Definition, Types & Usage Rules

There was no punctuation in any languages of ancient times. With the advancement of civilization, punctuation was introduced in the written form of the language to help a reader distinguish words and ideas from each other and to mirror the natural rhythms of the spoken language. This article will cover proper usage of some of the basic punctuations.
End Marks: Period, Note of Interrogation, Note of Exclamation

Period (.)
The period is also called full stop in England. A period declares the end of a sentence. It also indicates the separation of sentences so that the readers cannot mix up different sentences. A period is used at the end of a sentence which is complete and not a question or an exclamatory sentence.
Example:
Alex was a little boy when he first saw a person dying. He was so shocked and panicked that he could not sleep for several days. He still fears the sight of someone’s death.
The period is also used in abbreviations.
Example:
- Saint = St.
- Exempli gratia = e.g.
- Nota bene = N.B.

Note of Interrogation (Question Mark) (?)
The note of interrogation is used to complete sentences that form a direct question. Indirect questions are regarded as statements, and they take periods, not question marks.
Example:
- Have you had your breakfast?
- Where are you going?
- I don’t know where he is going. (A statement, not a direct question)
Do you know he was watching TV all day long while I was cleaning the house for the party that we want to throw on this weekend? (It’s a long sentence, yet it is a direct question.)
Did you once think about your family? Your career? Your future? Your life? (Series of questions using the same subject and verb)
Note:
What? – So? – Right? (Single word questions are used only in informal writing.)

Note of Exclamation (Exclamation mark/point) (!)
The note of exclamation indicates excitement, either positive or negative. It can also be used for giving additional emphasis to sentences, phrases, or single words, and especially to commands and interjections.
Example:
- Wait! Don’t take another step!
- I can’t believe she could say that!
- What a gorgeous house!
Note: It is best to avoid using a note of exclamation whenever the excitement can be described in words. You should be meticulous in using this punctuation in any form of writing.

Comma (,)
The comma is the most useful and common punctuation mark in English. It has many important roles in making a written form of English easy to read.
Commas usually add breathing scope for the readers in sentences, so that their thoughts cannot get all jumbled up. A comma has many uses.
i. Comma between Independent Clauses
Usually, a comma separates two independent clauses when they are connected by certain coordinating conjunctions (and, but, or, nor, or for). However, if the clauses are very short, no comma is needed.
Example:
- They finished dinner in pin-drop silence, but Alex knew that he would have to apologize.
- I wanted to watch a movie after dinner, but I could not tell her as I was confused about her reactions.
- We had dinner and then I watched a movie. (No comma is needed between these clauses)
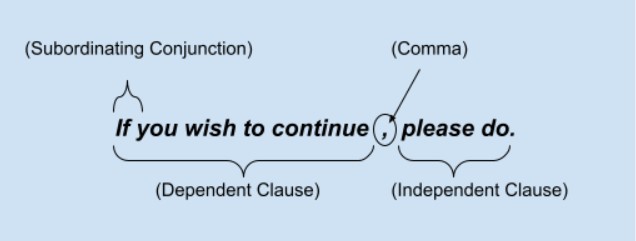
ii. Comma after Introductory Clauses, Phrases, and Expression
Commas are used not only between independent clauses but also after introductory clauses and phrases. Some expressions and connectors which are placed at the beginning of a sentence also require a comma after them.
Example:
- If you take off your jacket, you’ll catch a cold. (If the subordinators are used at the beginning of the sentences, the comma marks the separation of the two clauses)
- Being insulted, the piper went to the hill. (Participial phrases are always separated from the clauses by commas.)
- Before start riding it, you should read the instructions.
- When you came here, Alex was the general manager.
- Well, I cannot play in the next match.
- However, Alex will play in the next match.
- In winter we usually stay at home most of the time. (Short phrases like “in winter” don’t need commas.)
Note: A good way to clear the confusion about commas is to read the sentence aloud to make sure whether there is enough pause taken or not for using a comma.
iii. Series Comma
Commas are used to separate multiple items of the same category in a series. These items can be a series of words, phrases, or clauses.
Example:
- We brought pizzas, burgers, chocolate, and a chocolate cake on tour.
- The batsman set up his pads, put on his helmet, and played a good knock. (verb phrases)
- He is a player, a singer, an actor, and a director.
iv. Comma before Tag Question
Commas are used before a tag question which is usually a reassuring statement of a sentence’s overall idea.
- They’re ready to go, aren’t they?
- They’ll never do it, will they?
- He loves you, doesn’t he?
v. Comma in Direct Address
Commas are used in vocative uses. Calling someone by name or directly referring to them requires separation by commas.
Example:
- Hey, Joe, what are you doing?
- Listen, Lee, you have to bowl well today.
- You know, kid, when I was your age, I used to go out a lot.
vi. Comma for Adding Nonessential Ideas and Nonrestrictive Clauses
Commas can be used to add nonessential ideas or facts in the form of words, phrases, or clauses into a sentence. Usually removing these ideas from sentences does not affect the grammatical accuracy of the sentences.
Example:
- There’s a palace in London, just across the river, where I visited last week.
- The new player, you know him, scored a brilliant century.
- I suggest if that’s okay, that you let him go.
vii. Commas in Names and Dates
Commas are used to separate names of places and dates.
Example:
- Jefferson City, Missouri, is one of the biggest cities in the world.
- Brisbane, Queensland, is a big city.
- They were married April 05, 2013, in Melbourne. (No comma is necessary only for month and day – g., they were married on April 5 in Melbourne.)
- He was born June 24, 1993, in London.
viii. Commas in Dialog
Commas are used in the dialog to set off the indirect speech from the direct speech.
Example:
- I told him, “Don’t go there!”
- “When we were going there,” she said, “we saw thousands of palm trees.”
- “Please, give me that ball”, said the boy.
Common Mistakes with Commas
1. Commas do not separate two verbs or verb phrases joined by a coordinator.
Incorrect: I cleaned, and painted the box.
Correct: I cleaned and painted the box.
2. Commas do not separate two nouns, noun phrases, or noun clauses which are joined by a conjunction.
Incorrect: My coach, and our board president both sent letters.
Correct: My coach and our board president both sent letters.
3. Subordinate clauses do not need commas when they are joined by a conjunction between them.
Incorrect: I’ll be late if you don’t let me go now.
Correct: I’ll be late if you don’t let me go now. (If you don’t let me go now, I’ll be late.)

Colon (:)
Colons are the least used punctuation mark. The usage of colons is limited. Yet, if you know how to use them, you will be able to use them in your writing.
i. Colons are used in the salutations of formal letters.
Example:
- Dear Sir:
- To whom it may concern:
- To all members:
ii. Colons sometimes introduce a series/list to describe some new information after a complete sentence.
Example:
Incorrect: The fruit seller had: bananas, apples, and oranges.
Correct: The fruit seller had three kinds of fruit: bananas, apples, and oranges.
iii. A colon is also used to connect two independent clauses where the first one explains the second clause or logically follows it. The first word after a colon usually is not capitalized unless the colon introduces a series of new sentences or independent clauses.
Example:
- He was just thinking only one thing: what was his dog doing then?
- I knew the clue: you just had to read it in the mirror.
iv. Colons are used for expressing TIME in figures.
Example:
- 1:30 AM (Not o'clock)
- 7:35 PM
- 6:30 in the morning

Semicolon (;)
Semicolons are almost like periods, but they connect two independent clauses or sentences together instead of using a coordinating conjunction. Semicolons between the two clauses or sentences indicate that the clauses are closely related. Semicolons can be replaced by the coordinating conjunctions.
Example: We do not need a car now; we want to sell it. (This semicolon could be replaced by ‘and’.
Common transitional expressions such as therefore, for instance, namely, indeed, additionally, further, moreover, likewise, and finally are used after a semicolon to start a new clause.
Example:
- We used to love hunting; however, it is not legal
- He does not like me; likewise, I do not like him.
- It’s too cold out here; indeed, it’s winter.
Read More: Correct Use of Semicolons

Hyphen (-)
Hyphens combine words together to make Compound Nouns/Adjectives. Hyphens are also used with some suffixes and prefixes, such as -like, -wise, anti-, and post- to make new adjectives.
Example:
- Anti-violent
- Dog-like
- Ability-wise
- Decision-making
- City-owned
Compound numbers and continuous numbers require hyphen in them. A hyphen is used with compound numbers from 21 to 99 in words and with fractions which work as adjectives in the sentence. Fractions which are nouns don’t need hyphens.
Example:
- Sixty-five
- Twenty-five
- Their age is 23-25.
- William Shakespeare (1564-1616)
- Three-fifths full a glass
Dash (–)
A dash hints a brief break in thought or helps to add information to a sentence. A dash has no space before or after it.
Example:
- The man was running around the building—I couldn’t see his face—and disappeared down the alley.
- This house—and every house on the street—will be connected by this wire.
- Russel Crow—you know him, I think—is coming to our locality.
A dash can replace the conjunctions such as namely, that is, or in other words to add new information or explanation.
Example:
- I was thinking about another road—the one through New York.
- There’s only one way not to lose—don’t even participate in the game.
Apostrophe (’)
An apostrophe indicates possession and the exclusion of letters in contractions.
Example:
- They’re going to Canada.
- I’m not going.
- Robert’s watch
- Someone's glasses
- Trees’ leaves (If there is an ‘s’ before the apostrophe, no ‘s’ is needed for it)
- Teams’ scores
- Jones’ pen
Quotation Marks (‘...’/“... ... ..”)
Quotation marks are used for enclosing direct quotations of written or spoken words of others, or dialog said by characters in fiction.
They are also called quote marks or just quotes for short. The first of the pair is the opening or open quote. It curves to the right: “ ‘. The second one is the closing or close quote. It curves to the left: ’ ”.
Example:
- Have you seen the music video for the song “Despacito”?
- “Play with aggression” shouted the coach.
- Your exact words were “get out of my room.”
- “I'd never dreamed that I'd lose somebody like you”–this line from the song ‘Wicked Games’ always makes me sad.
Notes:
- Commas and periods must always be placed inside the quotation marks, according to most citation systems.
- Colons, as well as, semicolons, on the other hand, should be placed outside the quotation marks.
- Note of interrogation and note of exclamation should be placed inside the quotation marks when they are part of the quoted elements. Seemingly, when the note of interrogation and exclamation are not a part of the quoted materials, they are not placed outside the quotation marks.
Parentheses - ()
Parentheses block off materials that interrupt the text to add information.
Example:
- The parks (in Boston) are always crowded.
- We provide a lot of services. (See our website)
- We provide a lot of services (see our website).
Brackets
Brackets enclose the additional things in the quoted material. These additions are used for clarifications of the words or phrases of the quoted materials.
Example:
- “It [the river] taught me all I ever knew about life.”
- “Yeats used to love her [Maude Gonne], and he wrote many poems about her.”
- “Every man[sic] must die one day.”
- “I told [Spielberg] I wouldn’t do the movie.”
Brackets are also required to block off materials that fall within materials which are already enclosed by parentheses.
Example:
- We provide a lot of services. (See the website [Table 23] for the details)
Grammar
Read More
- How to Use "Therefore" in Sentences Avoiding Common Mistakes
- How to Use "Whereas" with Examples and Avoid Common Mistakes
- When and How to Use "Thus" Correctly Without Common Mistakes
- How to Use "On the Contrary" Properly with Meaning and Examples
- When and How to Use "Either/Or" with Examples and Common Mistakes to Avoid
- How to Use "On the Other Hand" Effectively without Mistakes
- How to Use "Respectively" with Example and Common Errors to Avoid
- How and When to Use "Moreover" Without Mistakes
- How to Use "Likewise" in Sentences Based on Context & When not to Use
- When & How to Use "Although" in Sentences to Avoid Mistake